Alumina Ceramic
Wear Resistance by Alumina Ceramic in Coal Mill Pulverizer and Pipe Line
Erosion is caused by pressurized air which carries entrained abrasive solid coal particles, impinging on a surface. When the angle of impingement is less than 30 deg, the wear produced is closely analogous to abrasion. When the angle of impingement is more than 30 deg to the surface, particle from mill internals is dislodged by impact erosion.
Alumina Ceramics are used in a very broad range of wear resisting surfaces and for the repair of wear resisting surfaces of coal mills. Indeed, these alumina liners do provide the best solution for giving the desired performance.
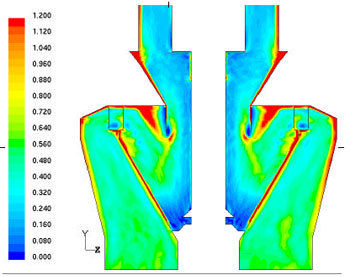
A study was conducted for erosion pattern of coal mill internals due to coal flow in vertical spindle pulverizers in PC Boilers. The coal and air mixture makes a number of turns before it reaches the Multiple Port Outlet. The changes in direction of flow cause the majority of coal particles to accumulate in the "Red marked" portion of the pulverizer as under:
Coal Flow Concentration Distribution within the model Pulverizer
Accumulated coal particle has abrasive wear mechanism, basically same as machining, grinding, polishing or lapping that we use for shaping materials. Two body abrasive wear (coal dust and mill internals) occurs when one surface (coal- harder than the metal mill internals) cuts material away from the mill body and internal, this mechanism very often changes to three body abrasion as the wear debris then acts as an abrasive with coal dust on mill internal surfaces. This abrasion can be reduced to great extent by fixing Alumina Ceramic Liners on high coal accumulation areas.
Based on the above study BMW has developed Alumina Ceramic Lined Mill internals, Multiple Port Out Let, Mill Discharge Valves, Coal flow Orifices, Coal Pipe and Bends. These are elaborated under the specific sections.